Convergence of Echolocation in the Common
Shrew
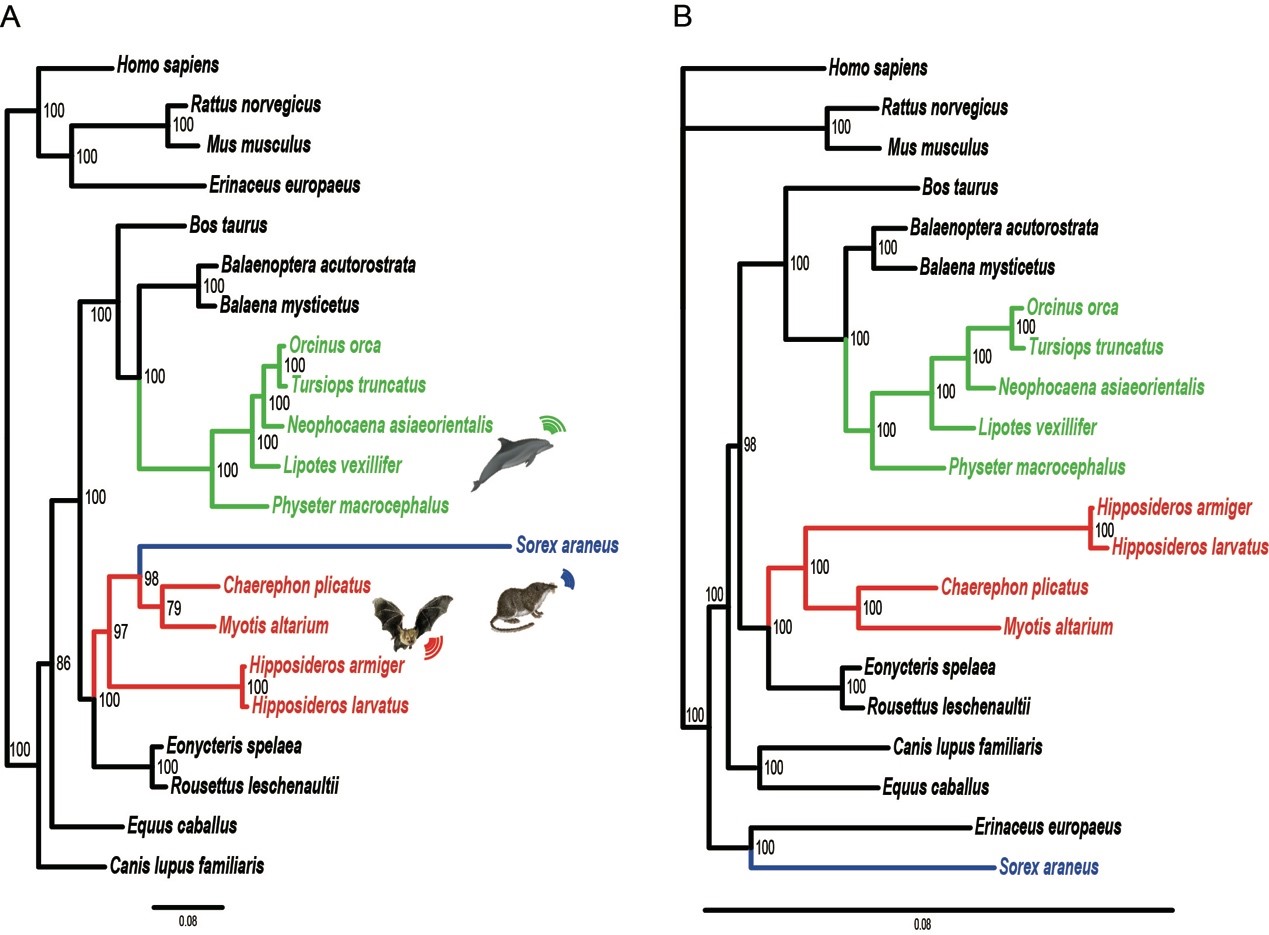
According to previous behavioral and experimental studies, the common shrew (Sorex araneus)
was indicated to echolocate by high-frequency twittering for
close-range spatial orientation, which is a convergent ability observed
in bats and whales. However, whether echolocation in the common shrew
is convergent with bats and dolphins at the molecular level remains
poorly understood. Here we collected CDS of 11 hearing-related genes
and performed evolutionary analyses. We found a set of amino acid
residues under strong convergent evolution shared among the common
shrew and other echolocating mammals. Furthermore, Sorex araneus
converged with echolocating bats in a gene tree based on the combined
amino acid dataset of convergent shift. This study provides evidences
of simple echolocation in Sorex araneus at molecular level and novel insights into the convergent evolution between the common shrew and sophisticated echolocators.
Read the full article, published by Zoological
Studies, here
Follow Zoological Studies on
Twitter @ZooStudies
and Facebook
