Impacts of Prey Depletion and Climate Change on Predator-Prey Dynamics in Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve
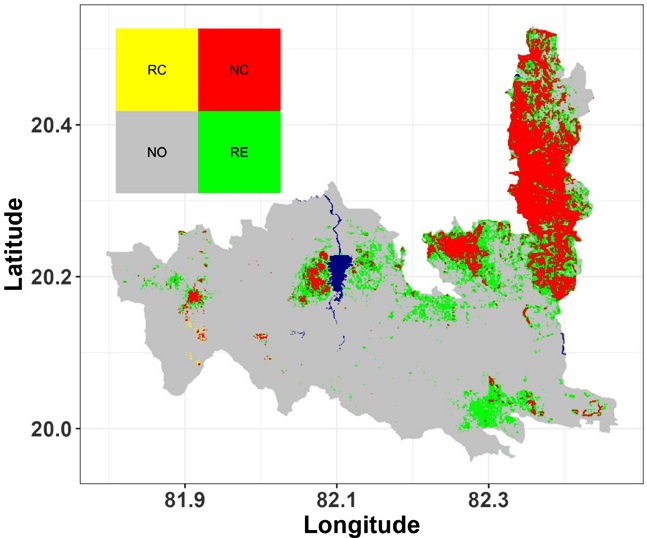
This study explores trophic cascades and habitat suitability in Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR) using the Trophic Species Distribution Model (Trophic SDM) and climate projections. It highlights the crucial roles of apex predators, subordinate predators, and prey in sustaining ecosystem balance and projected significant regional habitat shifts that is calling for adaptive management. Focusing on community participation, anti-poaching efforts, and science-based strategies is essential for long-term conservation success in this critical tiger landscape. Key conservation priorities include habitat restoration, prey augmentation, and predator recovery to sustain the reserve's ecological purpose and the Chhattisgarh-Odisha Tiger Conservation Unit’s potential. This comprehensive analysis underscores the critical role of targeted conservation activities in prey-depleted landscapes to ensure the long-term survival of tigers and the overall health of forest ecosystems, enhancing biodiversity and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts in USTR.
Read the full article, here

