Contrasting Benthic Invertebrate Community Shifts After Extreme Rainfall
This study assessed benthic community changes at Shanfu (SF) and Duozaiping (DU) reefs on Liuqiu Island from 2020 to 2022, following extreme rainfall in mid-2021. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) varied from −1.83 (indicating severe drought) to +1.90 (indicating severe precipitation) during the period 1997-2022. SF and DU differed significantly in diversity metrics, with site-specific factors exerting a stronger influence than interannual variation. Notably, DU showed marked shifts after the rainfall event, primarily driven by changes in echinoderm populations—likely a result of prolonged stress across the broader reef flat. These findings underscore the site-specific vulnerability of reef communities and offer valuable insights for developing targeted reef management strategies in response to climate change.
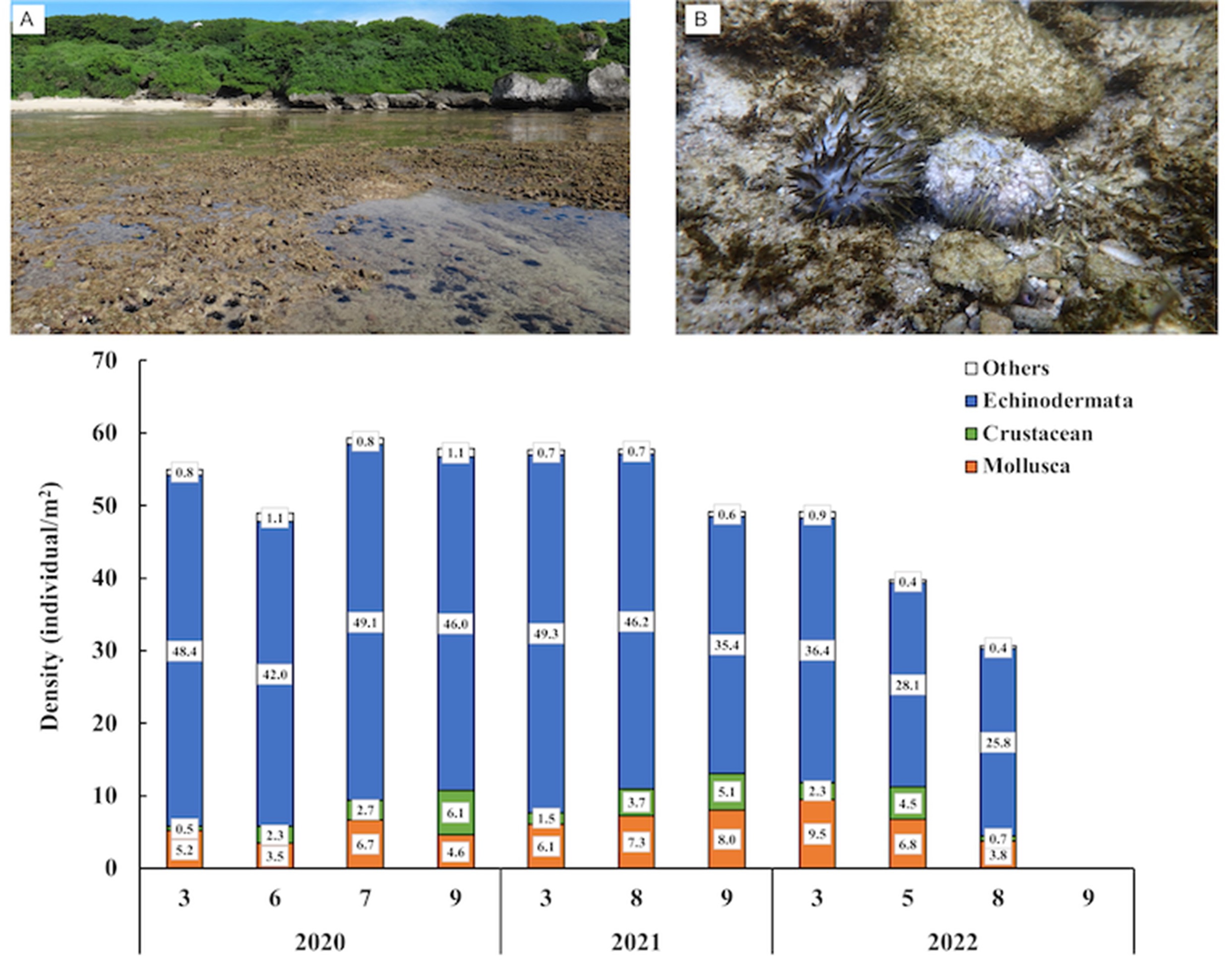
Dead sea urchins and density of benthic invertebrates at Duozaiping intertidal zone in Liuqiu Island.
Photo credit by Li-Lian Liu and Wei- Cheng Lai.
Read the full article, here

